Cross-linked monomers commonly used in acrylic emulsion
In order to give emulsion polymers more excellent tensile strength, hardness, wear resistance, adhesion strength, water resistance, alkali resistance, solvent resistance, heat resistance and dirt resistance, The linear emulsion polymer is often cross linked to form a three-dimensional reticular structure.
The most commonly used method is to introduce a monomer with a cross-linked functional group in a copolymerized monomer, so that the obtained emulsion copolymer has a crosslinking group on the molecular chain. In the subsequent polymer emulsion forming process, under certain conditions, crosslinking polymer is formed by cross-linking chemical reactions between the groups on the molecular chain of polymer. Or through the chemical reaction between the crosslinking group and the external crosslinking agent on the molecular chain, the crosslinking bond is formed to form the crosslinked polymer.
Several types of commonly used crosslinking monomers are:
1. Multiple double bond cross linked monomers
This type of crosslinker has at least two double bonds. When emulsion copolymerization was used as a comonomer, due to the space obstacle, most of the cross-linked monomer molecules had only one double bond involved in polymerization, forming only mild crosslinking emulsion polymer. In the subsequent film forming process, further cross-linking is further carried out under higher reaction conditions. For example, 1-but-3-enyl-2-ethenylbenzene.
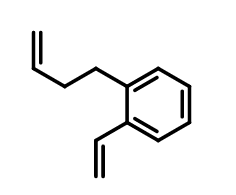
1-but-3-enyl-2-ethenylbenzene
2. Carboxylic acid crosslinked monomer
This kind of crosslinked monomer is a double bond carboxylic acid with a carboxyl group on the molecular chain of the copolymer, which provides a crosslinking point for the crosslinking reaction. Of course, there is no cross-linking reaction between these carboxyl groups. It needs to react with the molecules on the molecular chain or with the hydroxyl group, epoxy group and metal ion on the molecular chain, so as to form cross-linking structure. Carboxylic acid type crosslinking common monomers are acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, itaconic acid, maleic acid, fumaric acid, etc..
3. N substituted acrylamide derivatized crosslinked monomers
In the process of emulsion polymerization, a copolymerization monomer is added to the reaction system to introduce hydroxyl groups on the molecular chain of the copolymer. During the subsequent film-forming process, hydroxyl groups react with other groups on the molecular chain, such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, amino and Xian Anji, and form condensation bonds.For example, N-(2-methylpropoxymethyl)prop-2-enamide
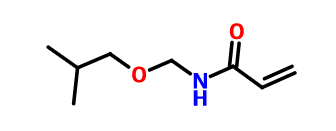
N-(2-methylpropoxymethyl)prop-2-enamide
4. Hydroxyl type crosslinked monomer
The cross-linked monomer has double bonds and hydroxyl groups at the same time. It acts as a comonomer and participates in the emulsion copolymerization. It introduces hydroxyl groups to the molecular chains of copolymers. In the subsequent film-forming process, under certain conditions, hydroxyl can react with other groups, such as carboxyl group, amino group and epoxy group, or crosslinking reaction between hydroxyl group and external crosslinking agent to form crosslinked polymer. For example, hydroxyethyl acrylate.
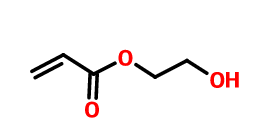
2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate
5. Epoxy crosslinked monomer
There are both double bonds and epoxy groups on the crosslinked monomer. During the subsequent emulsion forming process, the epoxy group can react with the carboxyl group, amino group and hydroxyl group on the molecular chain or the crosslinking agent molecules, and produce a bonding bond. The commonly used epoxy type crosslinked monomers include glycidyl methacrylate, glycidyl acrylate and allyl glycidyl
.
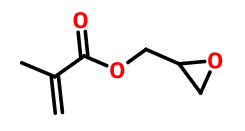
Glycidyl methacrylate
6. Carbonyl carbonyl crosslinked monomer
The crosslinked monomer is a compound with double bonds and carbonyl groups on the same molecule. There is no crosslinking reaction between carbonyl groups. If two or multiple hydrazine is added, the carbonyl group can react with the carbonyl group at room temperature. For example, diacetone acrylamide (DAAM) and two Acylhydrazine (ADH) adipate (ADH) can have crosslinking reaction at room temperature.
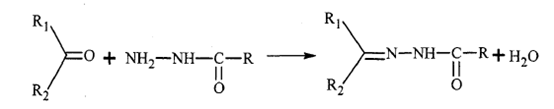
Reaction equation